Formulation Development for Injectables: From Molecule to a Reliable Dosage Form
A sterile injectable touches many lives quietly. A tiny volume travels through a syringe or a vial, enters the bloodstream, an eye, or a joint, and is expected to perform with absolute consistency. That small volume hides a large story. Solubility choices determine whether the active stays in solution through storage and during administration. Osmolality and pH influence comfort and local tolerance. Surfactants protect interfaces but can trigger particles when stressed. A stopper or a needle can shed micro-particulates. The lyophilizer shelves hold a careful temperature map that makes the difference between a cake that reconstitutes quickly and one that crumbles. In brief, formulation development for injectables is not a single experiment. It is a sequence of linked decisions that protect safety and performance while remaining viable for manufacturing and regulatory scrutiny.

Regulatory expectations for sterile products have risen in recent years. Contamination control strategy, cleanroom discipline, and a lifecycle view of sterility assurance are now routine expectations. Pharmacopoeial chapters on particulate matter and bacterial endotoxins set explicit acceptance criteria and standard methods. Container closure integrity has moved from an afterthought to a routine program decision. These expectations shape how a development path is designed from the day the molecule is profiled to the day the first clinical batch is released.
Formulation development for injectables is also a practical craft. Early work screens solubility routes and excipient sets that can survive real handling. As knowledge builds, a development team locks down a design space that respects scale-up, equipment realities, and the chosen container closure system. The result is a drug product that remains physically and chemically stable, sterile, and usable by a nurse or a patient without surprises.
Connect with our scientific experts for your drug discovery, development and manufacturing needs
Overview of Formulation Development for Injectables
Overview
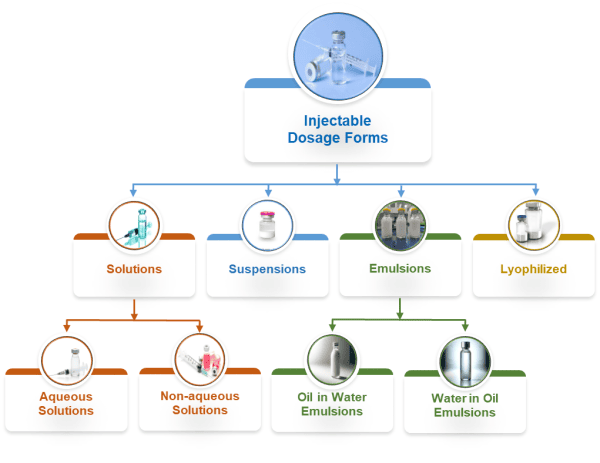
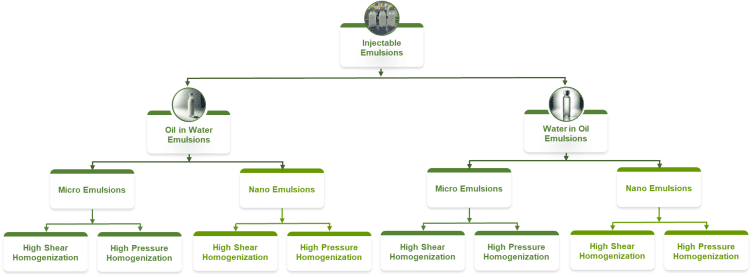
Injectables span several dosage forms that place different demands on formulation, process, and packaging. The choice depends on solubility, sensitivity to heat or shear, dose strength, and the intended route, such as intravenous, subcutaneous, or intramuscular. Each approach balances science and practicality so that the presentation is stable, sterile, and suitable for manufacture and use.
True solutions
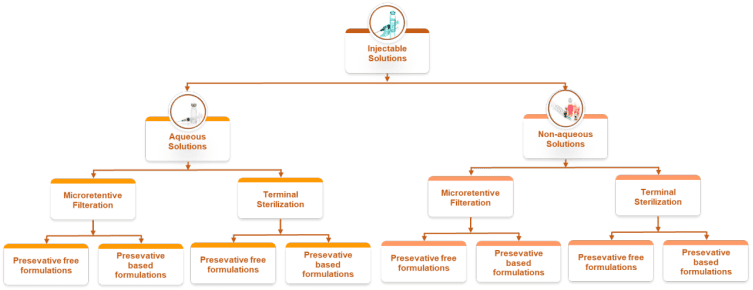
A true solution keeps the drug fully dissolved in an aqueous medium within a narrow pH and osmolality window that suits injection, yet this apparent simplicity hides strict operational control because even small shifts in pH, ionic strength, or temperature can trigger precipitation. Formulators typically use buffers like phosphate, citrate, or histidine to stabilize pH, add sodium chloride or dextrose for tonicity, and include antioxidants or chelators where oxidative liability exists, while surfactants are considered only when interface stress from mixing and filtration is expected. Processing focuses on oxygen control for sensitive actives, polishing filtration to remove particulates, tight bioburden limits, and validated sterile filtration, with terminal heat sterilization chosen only when the molecule tolerates it; the main risks are precipitation during storage or upon dilution, formation of subvisible particles at interfaces, and unwanted interaction with container materials.
Nonaqueous systems
When a molecule is highly hydrophobic or unstable in water, nonaqueous vehicles or cosolvent blends provide solubility and protect against hydrolysis, but they must be balanced to avoid pain and tissue irritation on administration. Typical systems combine ethanol, propylene glycol or polyethylene glycol with fixed oils such as sesame, cottonseed, or medium chain triglycerides, sometimes aided by solubilizers like polysorbates or poloxamers, and protected with antioxidants for oils. Manufacturing requires close control of solvent composition and moisture, careful oxygen management for unsaturated oils, and filtration methods compatible with the vehicle, while sterilization usually relies on sterile filtration and aseptic filling because terminal heat can drive solvent loss or degradation; key risks include injection site pain, hemolysis with certain cosolvents, evaporation that shifts concentration, and interactions with elastomers.
Suspensions and nanosuspensions
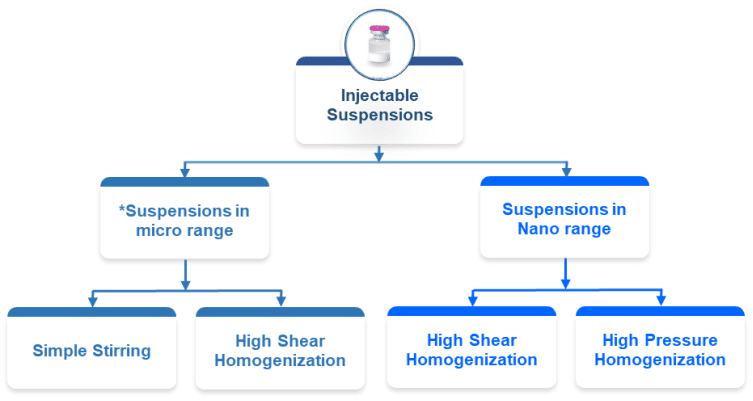
Suspensions deliver the drug as solid particles dispersed in a liquid vehicle, and nanosuspensions push particle size into the submicron range to improve injectability and sometimes bioavailability, but performance depends on good wetting, controlled size distribution, and resistance to caking so that a uniform dose can be drawn every time. Excipients are selected to manage interfaces and settling behaviour, with wetting agents like polysorbates or lecithin, and viscosity builders such as cellulose derivatives or poloxamers used to slow sedimentation without making the product hard to inject. Processing typically uses milling or high-pressure homogenization to reach the target size, followed by deagglomeration, controlled addition order, and deaeration, all under aseptic conditions since the particles often cannot withstand heat; the major risks are particle growth through Ostwald ripening, aggregation that clogs needles, and dose nonuniformity if resuspension is poor.
Emulsions
Emulsions combine immiscible phases as oil in water or water in oil, and are inherently unstable, so success depends on forming a fine and stable droplet size distribution with a robust interfacial film. Formulations usually place a pharmaceutically acceptable oil, such as soybean, safflower, or medium chain triglyceride, inside droplets stabilized by emulsifiers like phospholipids, polysorbates, or poloxamers, with the external phase adjusted for tonicity and pH. Manufacture starts with a high shear premix followed by high-pressure homogenization to reach the required droplet size while controlling oxygen and light for unsaturated oils, and sterilization typically proceeds by aseptic processing because heat can cause coalescence; long-term risks include droplet growth by coalescence or ripening, phase separation, and peroxide formation in oils, any of which can compromise safety and efficacy.
Lyophilized injectables
Lyophilization protects sensitive actives by freezing the solution and removing water under vacuum to create a dry cake that is reconstituted before use, thereby immobilizing structure in a glassy solid and limiting hydrolysis and aggregation during storage. Formulations often contain mannitol for cake strength, sugars like sucrose or trehalose for cryo and lyo protection, buffers that do not shift pH on freezing, and sometimes a surfactant to help during reconstitution. Development focuses on controlled freezing to set ice morphology, careful primary and secondary drying to reach target residual moisture, and checks on cake robustness and reconstitution time, all performed under aseptic conditions after sterile filtration; the main pitfalls are cake collapse, high residual moisture, slow or incomplete reconstitution, and particle formation during reconstitution.
Excipients and compatibility considerations
Across injectable forms, excipient selection is a balancing act that aligns chemical stability with patient comfort and device performance. Buffers govern pH within a range that protects the molecule yet avoids injection pain, tonicity agents bring osmolality near physiological levels, surfactants shield against interface damage but require control of their own degradation, and antioxidants or chelators are used only when the degradation pathway justifies them. Container closure choices then complete the system because glass type, elastomer chemistry, and lubricants influence leachables, adsorption, and particle formation, with prefilled syringes adding siliconization variables that must be controlled.
Sterilization and aseptic strategy
Sterility assurance is achieved by the best feasible route for the product, with terminal heat sterilization preferred when the drug can tolerate it, sterile filtration used for heat-sensitive solutions, and fully aseptic manufacture required for suspensions, emulsions, and lyophilized products. In every case, the approach is supported by validated filters or cycles, classified environments, rigorous environmental monitoring, and media fills that mirror real processing steps so that the sterility claim reflects actual practice rather than theoretical intent.
Process and in-use performance
Manufacturing aims to minimize shear and interfacial stress that drive aggregation or droplet instability, manage hold times to prevent growth or degradation, and control temperature and light through the workflow, while quality control monitors visible and subvisible particles with a bias for prevention at source rather than reliance on inspection alone. In practice, performance is verified through syringeability and injectability testing that measures the force needed to push the product through specified needles at controlled speeds, and the route of administration sets further constraints because intravenous delivery demands clarity and very low particulate burden, subcutaneous delivery limits volume and viscosity, and intramuscular delivery tolerates larger volumes but requires attention to pain and local reactions.
Choosing the right form
Selecting the right injectable form comes from a practical reading of the molecule's behaviour, the required dose, and the delivery setting. Solutions are preferred when solubility and stability allow, nonaqueous systems and emulsions enable very hydrophobic actives, suspensions keep insoluble drugs viable through controlled particle technology, and lyophilized products extend shelf life for fragile actives while easing transport. Whatever the path, the final product depends on coherent excipient choices, disciplined aseptic practice, compatible packaging, and a test plan that links laboratory results to real manufacturing and clinical use.
Solubility sets the ceiling for a true solution. If the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) will not dissolve at a practical pH and osmolality, the path shifts to cosolvents, complexation, micellar solubilization, or a nonaqueous vehicle. Any solubility map must respect comfort and safety limits as well as compatibility with the container and with the delivery route. For suspensions, the goal is not complete dissolution but a well-controlled particle size distribution that enables reliable dosing and acceptable in vivo dissolution.
Stability must hold across transport and use. Stress studies and accelerated conditions reveal hydrolysis, oxidation, Maillard reactions, or interface-driven aggregation for proteins and peptides. Freeze-thaw cycles and light exposure tests inform packaging and labeling for protection. For lyophilized products, thermal analysis and freeze-dried microscopy guide cycle development to avoid collapse and to build a cake with the right pore structure for fast reconstitution.
Sterility assurance is a lifecycle discipline rather than a single test. Aseptic processing draws on environmental monitoring, media fills, operator qualification, and a contamination control strategy that spans facility design, gowning, cleaning, and material transfer. Terminal sterilization, when feasible, offers a strong safety margin but can be limited by heat or radiation sensitivity.
Particulate matter control covers both visible and subvisible ranges. Filtration, clean handling, compatible stoppers and syringes, and tight upstream controls reduce risk. Pharmacopoeial limits are verified with light obscuration and microscopic methods. Routine trending is as important as release testing because many particle issues emerge during scale-up or filling.
Pyrogenicity and endotoxin control rely on process design, high-quality water systems, depyrogenation steps, and careful selection of materials. Limits need justification and demonstration that excipients do not interfere with the assay. A practical view includes early, small-scale checks to uncover interference before formal validation.
Container closure integrity and compatibility need early attention. Vials, stoppers, prefilled syringes, and cartridges must maintain sterility and protect quality through shelf life. Integrity testing now complements sterility tests in most stability protocols. Extractables and leachables studies, adsorption risk evaluations, and siliconization control round out the picture and reduce late surprises.
Scale up requires design spaces that travel. Shear rate can be a better scaling parameter than agitator rpm. Heat and mass transfer surrogates help translate lab steps to pilot equipment. A formulation that is stable at the bench but requires a narrow shear zone or a unique hold condition may not survive tech transfer. Early contact with the intended filling line and lyophilizer avoids late rework.
Quality by design ties all these strands together. Critical quality attributes guide risk assessments and experiments. The objective is a product and process that meet specifications reliably over time, not just a set of passing lots in development.
General Offerings of CDMOs
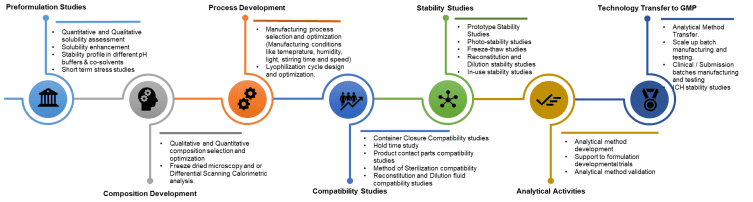
Early understanding and preformulation
The first job is to learn how the molecule behaves. Work starts with solubility and pH mapping across pharmaceutically acceptable ranges to see where the drug dissolves well without causing discomfort or instability. Osmolality limits, buffer choices, and practical pH windows are logged so that later formulation decisions stay inside a safe and comfortable space. If the active struggles to dissolve, cosolvents, complexing agents, micelles, or oil-based systems are explored at a small scale to understand feasibility without committing to a path too early.
Excipient screening then builds the simplest recipe that protects the molecule and remains suitable for injection. Buffers, tonicity agents, surfactants, antioxidants, chelators, bulking agents, and cryo or lyo protectants are evaluated for compatibility, function, and regulatory comfort. Interference with analytical methods is checked upfront so that assay and impurity results remain reliable. For proteins or peptides, interface stress, agitation, and silicon oil interactions are reviewed early because these often drive aggregation or particle formation later.
Short stress studies follow to expose weak points quickly. Heat, light, agitation, and freeze and thaw cycles reveal likely degradation routes and help prioritize controls. For candidates that may be lyophilized, thermal analysis and freeze-dried microscopy provide glass transition and collapse information that guides cycle design. Data from these small experiments are used to decide whether a true solution, a suspension or nanosuspension, an emulsion, or a lyophilized presentation is realistic for the program.

Route and presentation scoping pulls the findings together into a practical shortlist. Container and closure options, such as vials or prefilled syringes, are considered alongside the likely sterilization approach and filtration strategy. Early checks on contact materials, filters, and tubing reduce surprises during scale-up. The outcome of preformulation is a ranked set of feasible compositions and processes with clear notes on risks, open questions, and the quickest experiments that will answer them.
Formulation design and optimization
With a direction chosen, composition selection focuses on a recipe that meets comfort, stability, and manufacturability needs while remaining as simple as possible. The order of addition, mixing times, temperatures, and hold times is defined so that batches behave the same way regardless of operator. For suspensions and emulsions, particle or droplet size targets are set, and the process is tuned to achieve them consistently. Lyophilization feasibility turns into a real cycle using thermal endpoints and microscopy so that the cake structure supports fast and clean reconstitution. Throughout this phase, the team balances laboratory convenience with the realities of filtration, filling, and container compatibility, so the design does not stall during transfer.
Sterility assurance and microbiology
Aseptic process design is mapped early to show how materials, equipment, and people move through clean spaces without adding risk. Bioburden control and filtration strategy are defined so that microbial load stays low and sterilizing filters do not remove the drug or change critical attributes. Compendial sterility and endotoxin tests are set up with interference checks from excipients. Media fills, environmental monitoring, and operator qualification demonstrate that procedures can run reliably under cleanroom conditions. Container closure integrity is verified so that sterility is protected through shelf life and through typical temperature or pressure changes during shipping.
Analytical sciences
Analytical methods are developed to measure what matters for the product. Assay, impurities, pH, osmolality, residual solvents, particulate matter, and, when needed, protein attributes such as aggregation are included with clear system suitability criteria. Validation then shows that each method is specific, accurate, precise, linear, robust, and fit for its intended range. When testing will occur at another site, method transfer is planned so that results match across locations. The analytical target profile keeps all laboratories aligned on what each test is supposed to tell and what acceptance limits mean for real decisions.
Compatibility and materials control
Risk from materials that touch the product is managed step by step. Extractables and leachables planning looks at elastomers, plastics, lubricants, and adhesives to understand what might migrate and whether that migration matters. Contact parts such as tubing, filters, tanks, and needles are checked for adsorption, interaction, or particle shedding so the product quality does not drift during processing. Container selection compares vial glass types, stopper formulations, and syringe barrels, including siliconization levels and needle geometry. Early evidence reduces later changes and supports a smoother review.
Stability and in-use performance
Prototype and accelerated stability studies guide the selection of a lead and a backup formulation. Trends in potency, impurities, appearance, particles, and pH are used to set controls that will survive long-term storage. Photostability and freeze and thaw studies show if light or transport conditions create risk. Reconstitution and dilution studies confirm that the product dissolves or disperses quickly, remains clear or uniformly suspended, and maintains potency when mixed with common diluents. In use stability defines how long a multi-dose vial or an infusion solution remains acceptable after first opening or dilution, so that instructions are practical for clinics.
Process development and scale-up
Design of experiments helps identify which parameters matter and where the safe operating window sits. Scale-up rules translate bench steps to pilot and clinical equipment using simple engineering surrogates such as shear rate and heat transfer rather than only agitator speed. Hold time studies confirm that realistic pauses in manufacturing do not harm quality. Visual inspection criteria and defect libraries are established so that particulate and cosmetic checks remain consistent between operators and batches. The goal is a process that behaves predictably across different vessels and filling lines.
Technology transfer and clinical supply
A complete documentation package is prepared with master batch records, standard procedures, and training materials that reflect the established design space. Engineering and clinical batches are executed on qualified equipment while data are captured in a traceable way for regulatory use. Primary packaging and labelling are finalized with clear fill volumes, headspace targets, stopper choices, and instructions for storage and reconstitution. Feedback from the floor is fed back into risk registers and process descriptions so the transferred process remains stable and auditable.
Cold chain and logistics
Shipping studies simulate vibration, temperature excursions, and pressure changes to show that the product survives real transport. Packaging choices such as secondary containers and cushioning are tested alongside sensors. Temperature monitoring plans define how routes are tracked and what to do if an alarm triggers. The result is a chain of custody and temperature history that can be defended during audits and that keeps product quality intact until administration.
Quality and regulatory services
Risk management runs through the program with failure mode reviews that link process controls to critical quality attributes. Regulatory authoring compiles the required module content for clinical trial starts and later submissions, with clear justifications for limits and methods. Change control and comparability plans are drafted so that any future update to a component or a process step can be evaluated with data rather than debate. Quality assurance oversight keeps documentation clean, deviations investigated, and conclusions supported by evidence.
Program management and communication
The development path is coordinated through integrated planning that aligns formulation, analytics, microbiology, and stability activities on a realistic timeline. Communication stays regular and factual so that decisions are taken with current data. Clear roles, meeting notes, and action trackers reduce confusion and rework. The emphasis is on transparency so that all parties understand progress, risks, and the next experiment that will unlock a decision.
Digital and documentation hygiene
Data integrity practice ensures that records are complete, legible, contemporaneous, original, and accurate. Traceability links batches, methods, instruments, and operators to each result, which makes audits cleaner and investigations faster. Electronic systems are configured to retain raw data, metadata, and audit trails so that conclusions can be verified long after a study is closed. Consistent templates and naming keep the file system navigable for scientists and reviewers.
Typical deliverables by phase
Feasibility produces solubility and stability maps, draft recipes, and an initial risk register that highlights what must be solved next. Development consolidates into a final composition, a process description with operating windows, qualified analytical methods, and a first view of shelf life based on trend data. Clinical readiness adds validated methods, executed stability on representative batches, container closure integrity evidence, complete batch records, and submission-ready documents. By the end of this path, an injectable is not just a set of test results. It is a controlled recipe and process that can be reproduced, defended, and scaled with confidence.
What Aurigene offers
Aurigene develops sterile injectable products in solutions, non-aqueous solutions, suspensions, including nano options, emulsions, and lyophilized formats. Support covers early understanding, formulation, and process development, analytical methods, stability work, and transfer to cGMP for clinical or submission batches. The Hyderabad lab is equipped for developmental and pilot supportive work, with packaging in vials and glass prefilled syringes. Quality and regulatory teams handle documents and queries, and technical staff assist on-site during scale-up at client-chosen CMOs.
- Formulation development laboratory in Hyderabad with a pilot supportive lyophilizer and counter-pressure autoclave
- High shear mixers, dosing pumps, laminar air flow systems, and jacketed manufacturing vessels of one, two, and five litres
- Headspace oxygen analyser, freezing point depression osmometer, conductivity meter, pH meter, and dissolved oxygen meter
- Validated stability chambers for accelerated and prototype stability studies
- Primary packaging support for vials and glass prefilled syringes across typical ranges
- Preformulation studies including solubility mapping, pH stability, co-solvent assessment, and short-term stress studies
- Composition selection and optimization for solutions, suspensions, emulsions, and lyophilized products
- Freeze-dried microscopy and differential scanning calorimetry to inform cycle design
- Process development with parameter optimization, hold time studies, and sterilization mode selection
- Container closure, product contact part, filter compatibility, and filter validation studies
- Reconstitution and dilution studies, photostability, freeze-thaw, and in-use stability studies
- Analytical method development, optimization, validation, and method transfer across sites
- Technology transfer to cGMP facilities, scale-up support, clinical or submission batch manufacturing and testing
- Preparation of CTD content, risk assessments, and regulatory query support
- End-to-end development of sterile injectables across solutions, suspensions, emulsions, and lyophilized formats
- Lyophilization cycle design that balances cake structure, reconstitution time, and overall cycle length
- Practical focus on manufacturability, particulate control, endotoxin risk reduction, and container closure integrity
- Experience coordinating with external CMOs for engineering and clinical batches under cGMP
- Integrated quality and regulatory oversight across the development lifecycle
Note: The entire Product development program at Aurigene is supported by Quality Assurance and Regulatory Affairs teams. In addition, Aurigene supports for Regulatory filings and query response.
Challenges and Future Outlook
Contamination control under stronger oversight
Expectations for contamination control strategy, environmental monitoring, and data-driven reviews have increased. Development programs now need to show that contamination risk thinking is embedded from feasibility through scale-up. The practical response is to push risk assessments and operator training earlier, and to base decisions on routine trending rather than episodic checks. As analytics become more connected, deviations can be contained faster, and root causes can be narrowed more reliably.
Container closure integrity and lifecycle flexibility
Container choices can change after approval due to supply dynamics or performance improvements. Integrity data and deterministic test methods are now common in stability protocols. Development teams collect more evidence early and document rationale thoroughly so that post-approval changes are smoother. This will continue as more programs shift to prefilled syringes and novel elastomer or coating choices.

Particle and endotoxin vigilance
Subvisible particles and endotoxins remain leading causes of deviation and delay. Even when methods are standard, operational reality remains demanding. Silicon oil from syringes, agitation in shipping, and interactions with surfactants can drive particle counts. Endotoxin excursions can arise from water systems, raw materials, or insufficient depyrogenation. The outlook points to tighter process design, better compatibility with actual components, and real-time trending that catches drift before it affects release.
Lyophilization capacity and smarter cycles
Lyophilization demand is high, and capacity is tight in many regions. A better cycle design that reduces time without harming cake quality is a priority. Thermal mapping, controlled nucleation, and data-guided design spaces are being used to shorten primary and secondary drying. The direction is toward cycles that are robust to mild equipment variability, which improves throughput and reduces batch-to-batch differences.
Scale up resilience and design spaces that travel
Processes that look neat in development sometimes behave differently at pilot and commercial scale. Describing design spaces in scale-independent terms is becoming essential. More work is being invested upfront to define shear rate windows, residence time ranges, and temperature profiles that remain valid across equipment sets. This reduces friction at tech transfer and during post-approval changes.
Digital traceability and connected evidence
Sterility and quality are achieved on the floor, but digital records and analytics are changing the day-to-day experience. Environmental data, particle counts, and process parameters are being trended together to detect weak signals. Deviations are resolved faster when evidence is consistent and easy to query. Over time, this supports continuous improvement and a quieter deviation profile during clinical and commercial supply.
A successful injectable formulation balances many small, exacting choices. It accepts the constraints of patient comfort, container behaviour, and sterile processing. It respects compendial limits and regulator expectations without treating them as mere hurdles. It listens to stability signals early and builds a process that can travel across scales and sites. When a program works this way, a vial or a syringe stops being a risk and turns into a reliable bridge from molecule to therapy. Aurigene's capabilities and infrastructure fit into this disciplined path and can anchor the work from early understanding to qualified clinical supply.