We provide a wide range of antibiotic susceptibility testing services such as Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) tests in accordance with the guidelines issued by the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute using broth micro dilution, broth macro-dilution, disk diffusion and agar dilution methods.



Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC)
The MIC testing services for New Chemical Entity (NCE) helps determine the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial agent that prevents visible growth of a microorganism under defined test conditions.
We use the MIC values to evaluate the activity of new antimicrobial agents and to determine the NCE’s susceptibilities of microorganisms. MIC is considered as the ‘gold standard’ for determining the susceptibility of organisms to antimicrobials and is therefore used to judge the performance of all other methods of susceptibility testing.
Cultured microbes are incubated with the NCE at various concentrations and measured for the results using agar dilution or broth dilution methodology to determine the MIC endpoint. Agar dilution involves incorporating different concentrations of the antimicrobial substance into agar medium followed by the application of a standardized number of cells to the surface of the agar plate. For broth dilution, we often determine it in 96-well micro titer plate format, where microorganisms are inoculated into a liquid growth medium in the presence of different concentrations of an antimicrobial agent. Growth is assessed after incubation for a defined period of time (16–20 hours).
Susceptibility testing is typically conducted using organisms that contribute to an infectious process warranting antimicrobial chemotherapy. Several microorganisms such as aerobic or anaerobic bacteria, yeasts can be tested based on the requirement.
Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC)
The MBC testing services help determine the lowest concentration of an antimicrobial agent required to achieve bactericidal killing defined at 99.9% reduction in the initial inoculum. We chose it by sub-culturing broth dilution concentrations that inhibit the growth of a bacterial organism i.e. concentrations at and above the MIC. The broth dilutions are streaked onto agar surface and incubated for 24 to 48 hours. MBC is the lowest broth dilution of antimicrobial that prevents the growth of the organism on the agar plate. Failure of the organism to grow on the agar plate implies that all viable microorganisms have been eliminated.
Why Aurigene Minimum Inhibitory (MIC) and Minimum Bactericidal Concentration (MBC) Testing Services?
Submissions to the US FDA
Highly- qualified and experienced scientists
Audited by the US FDA with zero 483 in 2019
BSL-2 compliant microbiology lab
Connect with our scientific experts for your drug discovery, development, and manufacturing needs
We understand that clear communication is essential to successful collaborations, and that's why we have a dedicated team that is always ready to help you. Whether you have questions about our services, want to discuss a potential partnership, or simply want to learn more about our company, we're here to help.
Our team of experts is dedicated to providing personalised solutions tailored to your unique needs. So, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. We look forward to hearing from you and helping you achieve your business goals.
Learning Resources

JUNE 28, 2022
Neoantigen Specific T cells For Cancer Immunotherapy
An effective anti-tumor immune response in human is marked by presence of T cells reactive against neoantigens. Neoantigens are HLA-bound unique peptides arise from tumor-specific somatic mutations. Neoantigens are highly immunogenic because they are not present in normal tissues and hence bypass central thymic tolerance. The success of immune checkpoint blockade...
Read More
Accelerating Drug Discovery Through Innovative Partnerships
Genomics plays a vital role in identifying which gene is associated with a specific disease. A gene called CNOT1 is for example known for it's effect on brain development and for impairing memory and learning. Despite the great promise genomics provides in understanding the disease, genes are not the best drug targets....
Read More
Physiochemical Characterization Services
Backed by our strong chemistry, we enable “Finger-print” protein structure and functional characterization for proteins from naked proteins to hyperglycosylated or derivatized proteins. ...
Read More
Expediting early development through innovative precision capsule filling technology
Introduction: Any new chemical entity (NCE) needs to undergo various stages of development such as preclinical and clinical trials before drug product is approved by regulatory agencies and available for patient. Formulations developed during early phases are simple formulations to enable phase appropriate studies like screening, dose ranging, toxicological and d...
Read MoreAugust 28, 2020
Construction of a six-membered fused N-heterocyclic ring via a new 3-component reaction: synthesis of (pyrazolo)pyrimidines/pyridinesw
A conceptually new three-component reaction was developed to construct a six-membered fused N-heterocyclic ring affording (pyrazolo)pyrimidines/pyridines as potential inhibitors of PDE4. The reaction is catalyzed by triflic acid in acetic acid in the presence of aerial oxygen. ...
Read More-
January 31, 2025
Development and assessment of a Bcs class II - SGLT2 (Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2) inhibitor drug in the form of solid lipid Nanoparticles by selecting different lipids, co-surfactants, and manufacturing techniques
Drug Delivery System (DDS) has been used successfully in the past few decades to cure illnesses and enhance health because of its improved systemic circulation and ability to regulate the drug's pharmacological action. As pharmacology and pharmacokinetics advanced, the idea of controlled release emerged, demonstrating the significance of drug release in assessing...
Read More -
January 31, 2025
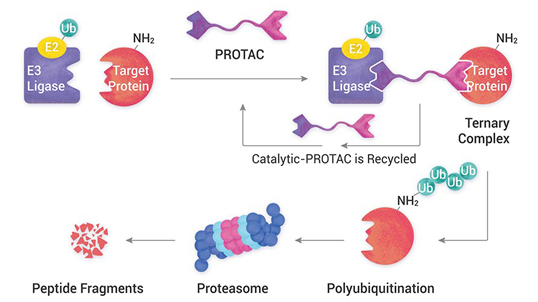
Development of novel paullone-based PROTACs as anticancer agents
Proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTACs) represents a promising modality that has gained significant attention for cancer treatment. Using PROTAC technology, we synthesized novel structurally modified paullone-based PROTACs using Cereblon (CRBN) and Von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) E3 ligands....
Read More -
March 13, 2025
Development and verification of RP-HPLC method for the quantitative determination of Decitabine in tablet dosage formulation
Decitabine is an anti-cancer chemotherapy drug. This article describes method development and method verification of Assay of Decitabine in tablet formulation. A new, precise, rapid, accurate RP-HPLC method has been developed for the estimation of Decitabine in pharmaceutical tablets dosage form. After optimization the good chromatographic separation was achieved...
Read More
You are about to leave Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services and affiliates website. Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services assumes no responsibility for the information presented on the external website or any further links from such sites. These links are presented to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement by Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services.
If you wish to continue to this external website, click Proceed.


Leaving already?
Don't forget to join us at
CPHI Worldwide 2023.
October 24th-26th, 2023 | Barcelona, Spain
Get ready to accelerate your drug’s journey to the market