Preclinical genetic toxicology studies are crucial for assessing the potential genetic risks of new drugs and chemicals before they are tested in humans. These studies help identify substances that may cause genetic mutations, chromosomal damage, or other genetic alterations that could lead to cancer or other genetic diseases. Here's a comprehensive overview of our capabilities at Aurigene:
- Mutagenicity Testing: To determine if a substance can cause genetic mutations.
- Clastogenicity Testing: To assess if a substance can cause structural changes in chromosomes.
- Genotoxicity Testing: To evaluate the overall potential of a substance to damage genetic material.


Why Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services?
Quick turnaround time
Extensive experience in the genetic toxicology studies
Team of expert analytical and toxicology scientists
State-of-the-art facilities
Connect with our scientific experts for your drug discovery, development, and manufacturing needs
We understand that clear communication is essential to successful collaborations, and that's why we have a dedicated team that is always ready to help you. Whether you have questions about our services, want to discuss a potential partnership, or simply want to learn more about our company, we're here to help.
Our team of experts is dedicated to providing personalised solutions tailored to your unique needs. So, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. We look forward to hearing from you and helping you achieve your business goals.
Learning Resources

JULY 02, 2021
Oligonucleotide as a novel class of therapeutic modality
Oligonucleotides as a therapeutic class is a revolutionary approach to discover new and important therapeutic agents for treating human diseases. RNA-based intervention at times works in cases where other modalities do not work. For example, it may help in treating inborn errors in metabolism, genetic disorders and rareOligonucleotide therapeutics is the use of c...
Read More
HPAPI Molecule from Development to Market
The global Highly Potent Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients (HPAPI) market is expected to reach USD 26.84 Billion by 2023 from USD 17.72 Billion in 2018, at a CAGR 8.7%....
Read More
Physiochemical Characterization Services
Backed by our strong chemistry, we enable “Finger-print” protein structure and functional characterization for proteins from naked proteins to hyperglycosylated or derivatized proteins. ...
Read More
Development of quick quantification method for muscle injury recovery evaluation in thermal injury mice model
Challenges: The evaluation of Evans Blue Dye (EBD) by fluorescence measurements of cryosections of individual muscle sections, and its quantification by auto fluorescence is a laborious and time-consuming process. Study design: Both sham and thermal injury techniques were followed. The evaluation of EBD was done to assess the effectiveness of two compounds in the...
Read MoreAugust 28, 2020
Construction of a six-membered fused N-heterocyclic ring via a new 3-component reaction: synthesis of (pyrazolo)pyrimidines/pyridinesw
A conceptually new three-component reaction was developed to construct a six-membered fused N-heterocyclic ring affording (pyrazolo)pyrimidines/pyridines as potential inhibitors of PDE4. The reaction is catalyzed by triflic acid in acetic acid in the presence of aerial oxygen. ...
Read More-
January 31, 2025
Development and assessment of a Bcs class II - SGLT2 (Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2) inhibitor drug in the form of solid lipid Nanoparticles by selecting different lipids, co-surfactants, and manufacturing techniques
Drug Delivery System (DDS) has been used successfully in the past few decades to cure illnesses and enhance health because of its improved systemic circulation and ability to regulate the drug's pharmacological action. As pharmacology and pharmacokinetics advanced, the idea of controlled release emerged, demonstrating the significance of drug release in assessing...
Read More -
January 31, 2025
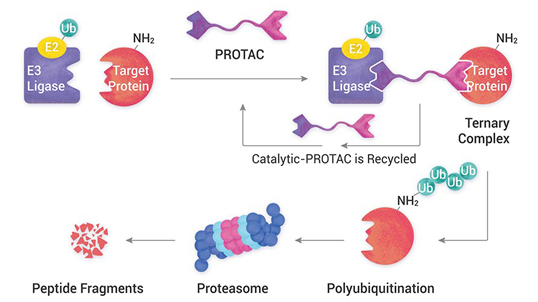
Development of novel paullone-based PROTACs as anticancer agents
Proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTACs) represents a promising modality that has gained significant attention for cancer treatment. Using PROTAC technology, we synthesized novel structurally modified paullone-based PROTACs using Cereblon (CRBN) and Von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) E3 ligands....
Read More -
March 13, 2025
Development and verification of RP-HPLC method for the quantitative determination of Decitabine in tablet dosage formulation
Decitabine is an anti-cancer chemotherapy drug. This article describes method development and method verification of Assay of Decitabine in tablet formulation. A new, precise, rapid, accurate RP-HPLC method has been developed for the estimation of Decitabine in pharmaceutical tablets dosage form. After optimization the good chromatographic separation was achieved...
Read More
You are about to leave Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services and affiliates website. Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services assumes no responsibility for the information presented on the external website or any further links from such sites. These links are presented to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement by Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services.
If you wish to continue to this external website, click Proceed.


Leaving already?
Don't forget to join us at
CPHI Worldwide 2023.
October 24th-26th, 2023 | Barcelona, Spain
Get ready to accelerate your drug’s journey to the market