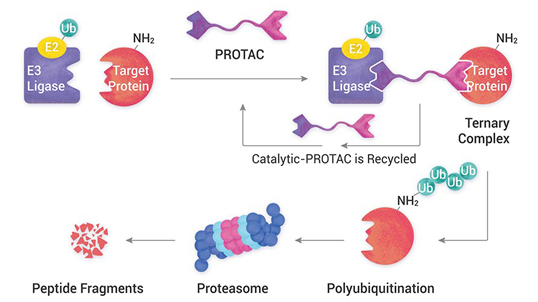
PROteolysis – TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs) are a series of hetero-bifunctional molecules that hijack the body’s own natural disposal system to initiate selective degradation of the protein of interest (POI). PROTACs have the potential to overcome most of the limitations of small molecule inhibitors, while offering several advantages of the traditional concepts of drug discovery. Aurigene offers expertise in all niche modalities related to PROTACs and molecular glues for targeted protein degradation, including stand-alone Chemistry, Biology (in vitro, in vivo pharmacology and toxicology) and DMPK services to fully integrated drug discovery programs.
We have extensive experience in not only the synthesis and purification of PROTACs but also the capability of extensively profiling our synthesized PROTACs including various biological assays, in addition to a full-spectrum ADME and PK services tailored to PROTAC molecules. We are uniquely poised in the Indian CRO market not only as a key player with extensive knowledge in small molecule-based Drug Discovery research but also can offer our significant experience on the PROTAC-related domain to any potential collaborators.
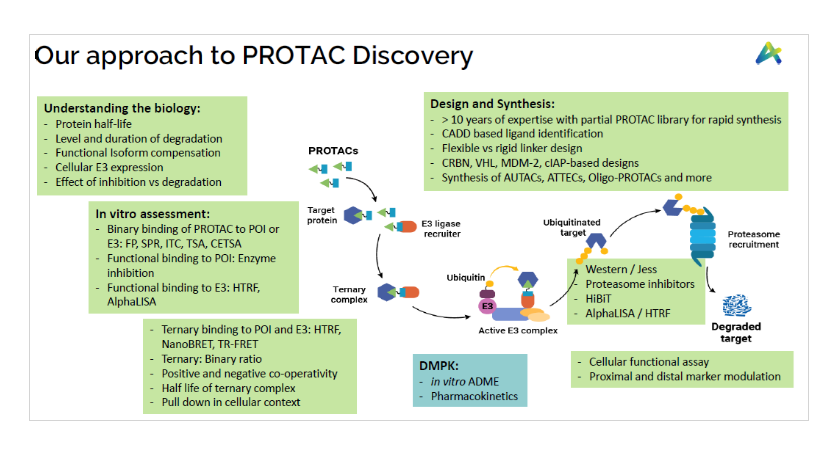
We are well versed in the synthesis and functionalization of various E3-ligase ligands such as CRBN, VHL, MDM2, AhR, and cIAP1 (in multi-gram scale) and in the synthesis of commercially available ligands, as well as in developing novel structural analogues as per custom requests like open CRBNs. We also have significant experience in the related fields of Targeted Protein Degradation (TPD) such as molecular glues, ATTECs, AUTECs, HyTs and in niche modalities like Oligo-PROTACs, Peptide-PROTACs, etc. We also offer a partial PROTAC library of ~500 entries as a quick plug-and-play for PROTAC development from a POI-ligand of choice.


PROTACs – Advantages over Conventional Inhibitors
PROTACs have the potential to overcome most of the limitations of small molecule inhibitors, and they offer several advantages of the traditional concepts of drug discovery, including increased selectivity and reduced toxicity among others. This approach also has the potential to target the “undruggable” proteome that limits traditional drugs.
PROTAC Synthesis and Screening Services for Targeted Protein Degradation
- Synthesis of common E3-Ligase ligands (CRBN, VHL, cIAP, and MDM-2) and their structural analogues from milligram to gram scale and beyond
- Capability to develop novel flexible or rigid linkers for novel discovery needs
- Experience in the synthesis of molecular glues and monovalent protein degraders
- In-house library of >500 partial PROTACs and linkers for rapid target engagement
- Flexible business models including stand-alone Chemistry services, as well as fully integrated discovery services and various mix-and-match programs
- Stand-alone biology support including in vitro and in vivo profiling, DMPK, or toxicology
Purification of PROTACs
- Synthetic team with >10 years of experience with PROTAC chemistry to minimize hurdles
- Very experienced analytical team, specifically in purifying PROTACs and Molecular Glues
- Dedicated preparative HPLC systems for supporting PROTAC-related projects
- Buchi Lyovapor L-300s for supporting the PROTAC platform in minimizing stability issues
- SFC and HRMS support provided wherever needed
Integrated Drug Discovery Expertise for PROTAC Screening
In addition to the Medicinal chemistry of PROTACs, Aurigene services also offer substantial experience in the biology of protein degraders, gained through the extensive in-house research drug discovery research. We offer comprehensive in-vitro biology support to interested collaborators, including various biological assays, DMPK and toxicology.
- Binary binding and functional assays to measure interaction of E3 ligase to PROTACs and PROTAC/ its ligand to target protein using various assays like TR-FRET, HTRF, AlphaLISA, and various other functional assays depending on the target protein and E3 ligase
- Target binding studies and ternary complex formation (using various assay platforms like Hi-BiT, Nano-BRET, SPR etc.) to understand the ratio of ternary to binary binding efficiencies
- Functional cell-based assays for evaluating target degradation (Western Blotting, Automated Westerns, HiBiT screening) and downstream target engagement assays
- Preliminary ADME studies (e.g. permeability, solubility, microsomal stability)
- PK studies in rodents (terminal) and in dogs (non-terminal studies)
- Fully integrated and semi-integrated drug discovery programs as well as stand-alone biology services.
- In addition to prosecuting PROTACs and screening, we also offer support at multiple levels to understand biology of target protein that includes protein half-life, extent and duration of degradation, functional isoform compensation (if any), cellular E3 expression, differential advantage of inhibiting the target vs degrading the target at molecular level and MoA studies.
Molecular Glues
- Molecular glues are monovalent small molecules (single entities) that reshape the surface of an E3 ligase receptor, assisting novel protein-protein interactions (PPIs) by squeezing between protein–protein interfaces (Schreiber, 2021).
- They are much smaller in nature and thus more easily abide by Lipinski’s rule of five, increasing the probability of good oral bioavailability.
- Expected to have better permeability and membrane uptake, more suited for CNS-targets.
| Type | Linker | Mol. Wt. | Lipinski Rule | Binding Pocket | Affinity | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PROTACs | Bivalent | Needed | >700-1000 | No | Needed | Strong |
| Molecular Glues | Monovalent | Not Needed | <500 | Yes | Not Required | Week |
At Aurigene, we have extensive experience in the synthesis and profiling of molecular glues, which provides us a unique advantage in offering stand-alone, semi-integrated and fully integrated discovery programs for our collaborators.
References
1. 1.Schreiber, S. L. (2021). The rise of molecular glues. Cell, 184(1), 3-9.
Why Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services?
Ready-to-use partial PROTAC library
Flexible business models including mix and match programs
Comprehensive biology support
Connect with our scientific experts for your drug discovery, development, and manufacturing needs
We understand that clear communication is essential to successful collaborations, and that's why we have a dedicated team that is always ready to help you. Whether you have questions about our services, want to discuss a potential partnership, or simply want to learn more about our company, we're here to help.
Our team of experts is dedicated to providing personalised solutions tailored to your unique needs. So, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. We look forward to hearing from you and helping you achieve your business goals.
Learning Resources

FEBRUARY 08, 2021
Introduction to PROTAC
PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras (PROTAC) are a series of hetero-bifunctional molecules that hijack the body’s natural disposal system to initiate selective degradation of the protein of interest (POI). They are generally bifunctional molecules that hijack the Ubiquitin Proteasome System (UPS) to achieve the total degradation of a disease-related target protein. ...
Read More
Accelerating Drug Discovery Through Innovative Partnerships
Genomics plays a vital role in identifying which gene is associated with a specific disease. A gene called CNOT1 is for example known for it's effect on brain development and for impairing memory and learning. Despite the great promise genomics provides in understanding the disease, genes are not the best drug targets....
Read More
Biologics Manufacturing Services
Our manufacturing services cater to both GMP and non-GMP manufacturing for pre-clinical development as well as GMP operation to support clinical or commercial needs for any recombinant proteins expressed in suspension mammalian culture or E. coli. ...
Read More
Expediting early development through innovative precision capsule filling technology
Introduction: Any new chemical entity (NCE) needs to undergo various stages of development such as preclinical and clinical trials before drug product is approved by regulatory agencies and available for patient. Formulations developed during early phases are simple formulations to enable phase appropriate studies like screening, dose ranging, toxicological and d...
Read MoreAugust 28, 2020
An efficient and convenient protocol for the synthesis of tetracyclic isoindolo[1,2-a]quinazoline derivatives
A convenient and one-pot synthesis of tetracyclic isoindolo [1,2-a]quinazoline derivatives via Lewis acid mediated sequential C–N bond formation reactions is reported. This protocol provides a simple and rapid strategy for the synthesis of 12-benzylidene-10,12-dihydroisoindolo[1,2-b]quinazoline derivatives. However, a variety of tetracyclo indole fused quinazol...
Read More-
January 31, 2025
Development and assessment of a Bcs class II - SGLT2 (Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2) inhibitor drug in the form of solid lipid Nanoparticles by selecting different lipids, co-surfactants, and manufacturing techniques
Drug Delivery System (DDS) has been used successfully in the past few decades to cure illnesses and enhance health because of its improved systemic circulation and ability to regulate the drug's pharmacological action. As pharmacology and pharmacokinetics advanced, the idea of controlled release emerged, demonstrating the significance of drug release in assessing...
Read More -
January 31, 2025
Development of novel paullone-based PROTACs as anticancer agents
Proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTACs) represents a promising modality that has gained significant attention for cancer treatment. Using PROTAC technology, we synthesized novel structurally modified paullone-based PROTACs using Cereblon (CRBN) and Von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) E3 ligands....
Read More -
March 13, 2025
Development and verification of RP-HPLC method for the quantitative determination of Decitabine in tablet dosage formulation
Decitabine is an anti-cancer chemotherapy drug. This article describes method development and method verification of Assay of Decitabine in tablet formulation. A new, precise, rapid, accurate RP-HPLC method has been developed for the estimation of Decitabine in pharmaceutical tablets dosage form. After optimization the good chromatographic separation was achieved...
Read More
Frequently asked questions
What is Target Protein Degradation?
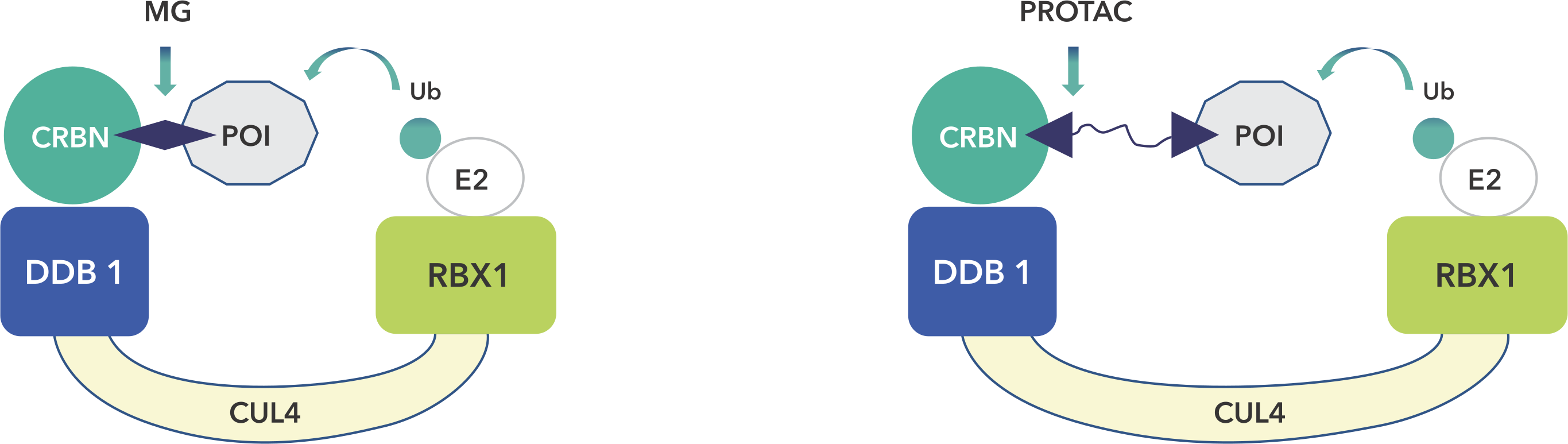
Target Protein degradation is a process in which the protein of interest is degraded using E3 ubiquitin ligase and a chemical linker by polyubiquitination followed by proteasome degradation.
What are the advantages of the Protein degradation approach against conventional approaches?
High target selectivity demonstrates high potencies, less toxic ,and minimizing the risk of developing resistance.
Does PROTAC forms a ternary Complex?
A targeting ligand (warhead) for the protein of interest and a ligand that recruits an E3 ubiquitin ligase connected via a carefully-chosen chemical linker (PROTAC). The resulting compound can induce formation of a ternary complex (the target, degradation compound and E3 ligase). The design of degrader compounds is critical to form an effective ternary complex.
What is Targeted Protein Ubiquitination?
The addition of ubiquitin to a substrate protein is called ubiquitination. Ubiquitination of target proteins involves a three-step enzymatic process, i.e., Activation, conjugation, and Ligation. Finally, polyubiquitinated proteins are recognized by the proteasome then degrades into small peptides by proteolysis.
What Is the PROTAC's Cellular Permeability and Target Affinity?
Cellular Permeability and Target Affinity are the important factors to decide the effective binding of PROTAC with target protein and ubiquitination. These parameters play a crucial role in the designing of PROTAC molecules.
What is the potential of PROTAC for pharmaceutical research?
PROTACs regulate protein function by degrading target proteins instead of inhibiting them, providing more sensitivity to drug-resistant targets and a greater chance of affecting nonenzymatic functions. PROTACs have been proven to show better selectivity compared to classic inhibitors. It has attracted great attention both from academia and industry.
How are PROTACs gaining traction as a cancer drug discovery technique in the modern era?
Catalytic in nature, targeted degradation and selectivity provide a niche for PROTAC applications in cancer diseases and immune disorders, viral infections, and neurodegenerative diseases.
You are about to leave Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services and affiliates website. Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services assumes no responsibility for the information presented on the external website or any further links from such sites. These links are presented to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement by Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services.
If you wish to continue to this external website, click Proceed.


Leaving already?
Don't forget to join us at
CPHI Worldwide 2023.
October 24th-26th, 2023 | Barcelona, Spain
Get ready to accelerate your drug’s journey to the market