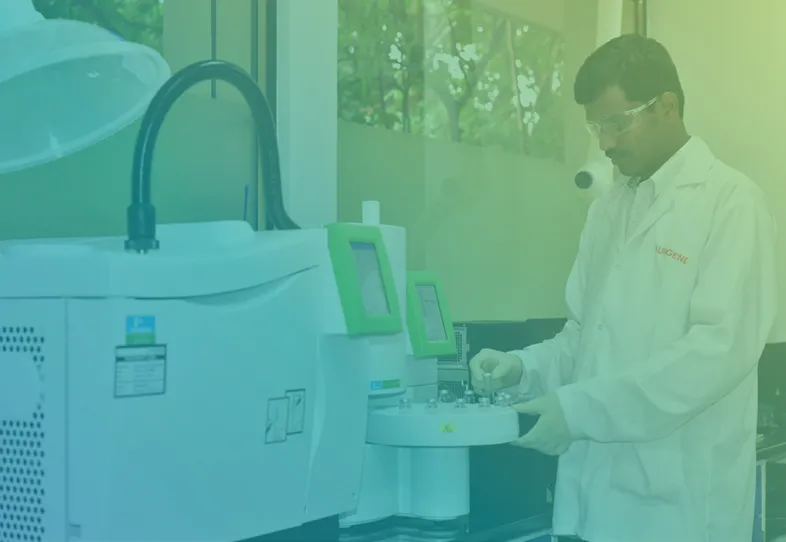
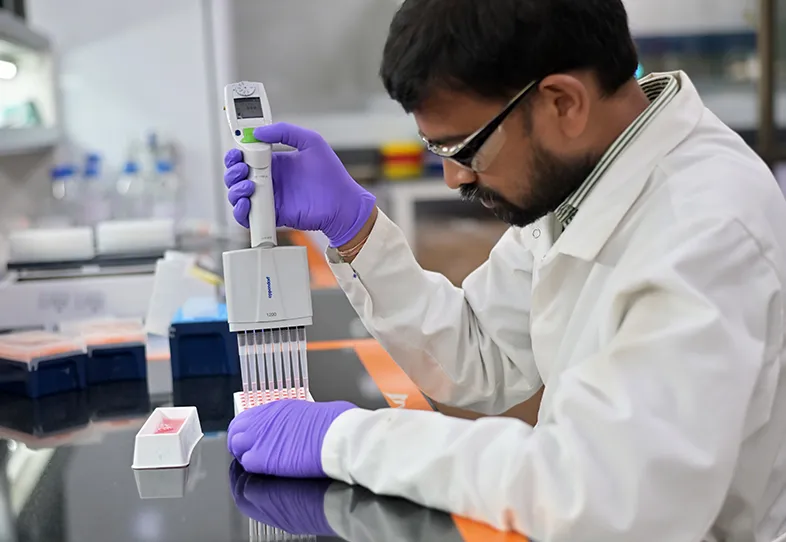
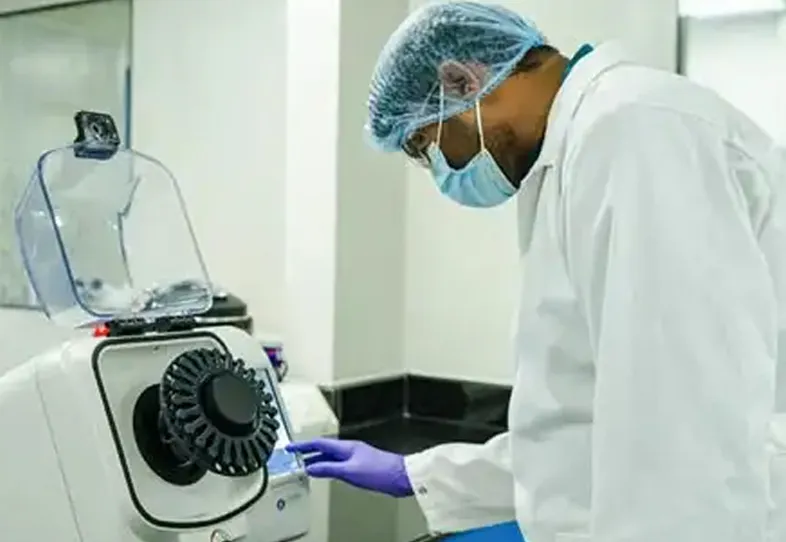
Aurigene offers GLP and Non-GLP bioanalysis services for small molecules, peptides, biomarkers and complex molecules. Our Bioanalytical labs are well-equipped with high-end LC-MS/MS instruments, HPLCs or UPLCs with UV, PDA and fluorescence detectors. We have completed more than 200 GLP studies. We perform sample analysis of GLP PK or TK or TD studies. We do method validation as per regulatory requirement and ensure data quality and compliance.






Why Aurigene GLP and Non-GLP Bioanalysis Services?
Delivered 200+ GLP studies
Compound management and data automation
Quality and Accuracy
Regulatory submissions to US FDA, EMA, DGCI
Connect with our scientific experts for your drug discovery, development, and manufacturing needs
We understand that clear communication is essential to successful collaborations, and that's why we have a dedicated team that is always ready to help you. Whether you have questions about our services, want to discuss a potential partnership, or simply want to learn more about our company, we're here to help.
Our team of experts is dedicated to providing personalised solutions tailored to your unique needs. So, please don't hesitate to reach out to us. We look forward to hearing from you and helping you achieve your business goals.
Learning Resources

JULY 02, 2021
Oligonucleotide as a novel class of therapeutic modality
Oligonucleotides as a therapeutic class is a revolutionary approach to discover new and important therapeutic agents for treating human diseases. RNA-based intervention at times works in cases where other modalities do not work. For example, it may help in treating inborn errors in metabolism, genetic disorders and rareOligonucleotide therapeutics is the use of c...
Read More
Evolution in Pharma Industry and Demand for Integrated CDMO
The pharma industry is evolving and a demand for integrated CDMOs, which can help accelerating innovations, is part of the evolution....
Read More
Developing a methodology for In situ perfusion based combined tissue distribution and toxicity evaluation study
Challenges: Several repeated in house validation studies were performed to optimize the suitable perfusate (liquid medium intended to pass through the heart), perfusate volume and perfusion rate to ensure complete perfusion of animal subjects (parameters weren’t adjustable) Challenges were encountered in adjusting the perfusion volume and rate vis-à-vis ensuri...
Read MoreAugust 28, 2020
Cu-catalyzed coupling-cyclization in PEG 400 under ultrasound: a highly selective and greener approach towards isocoumarins
The combination of CuI–K2CO3-PEG 400 facilitated the couplingcyclization of o-iodobenzoic acid with terminal alkynes under ultrasound, affording a greener and practical approach towards 3-substituted isocoumarins with remarkable regioselectivity. This inexpensive and Pd and ligand free methodology gave rise to various isocoumarins of potential pharmacological i...
Read More-
January 31, 2025
Development and assessment of a Bcs class II - SGLT2 (Sodium Glucose Cotransporter 2) inhibitor drug in the form of solid lipid Nanoparticles by selecting different lipids, co-surfactants, and manufacturing techniques
Drug Delivery System (DDS) has been used successfully in the past few decades to cure illnesses and enhance health because of its improved systemic circulation and ability to regulate the drug's pharmacological action. As pharmacology and pharmacokinetics advanced, the idea of controlled release emerged, demonstrating the significance of drug release in assessing...
Read More -
January 31, 2025
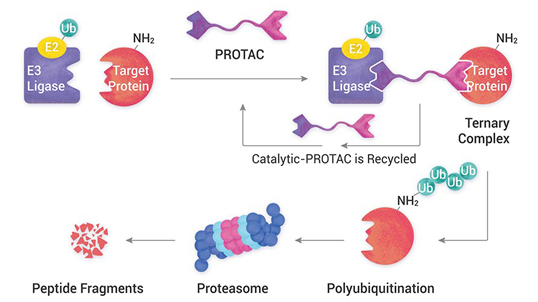
Development of novel paullone-based PROTACs as anticancer agents
Proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTACs) represents a promising modality that has gained significant attention for cancer treatment. Using PROTAC technology, we synthesized novel structurally modified paullone-based PROTACs using Cereblon (CRBN) and Von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) E3 ligands....
Read More -
March 13, 2025
Development and verification of RP-HPLC method for the quantitative determination of Decitabine in tablet dosage formulation
Decitabine is an anti-cancer chemotherapy drug. This article describes method development and method verification of Assay of Decitabine in tablet formulation. A new, precise, rapid, accurate RP-HPLC method has been developed for the estimation of Decitabine in pharmaceutical tablets dosage form. After optimization the good chromatographic separation was achieved...
Read More
Frequently asked questions
What is pharmaceutical development?
Pharmaceutical development identifies and evaluates processes required to convert an NCE/drug substance into a drug product to deliver for its intended performance/purpose consistently. The pharmaceutical development process begins by measuring drug substance properties, identifying critical attributes of the drug product, checking absorption and stability profile of the drug and the most appropriate route of administration (e.g. oral, parenteral or topical).
Why is pharmaceutical development important at early drug development stage?
Pharmaceutical development evaluation already at the early drug development stage is essential for selecting the right NCE and formulation to reduce the attrition rate in the late-stage development. These activities streamline efficacy/toxicology evaluations, allowing pharmacologically effective and developable molecules to reach the clinic and eventually patients.
What are the advantages of integrated early-stage drug development?
The integration and close collaboration of preclinical and clinical development teams accelerate the FIH product development process by utilizing already available pre-formulation and bioavailability information and experience gained during preclinical formulation development. It also helps identify obstacles and apply the right formulation strategies early in the drug development process to avoid costly late-stage failures, significantly saving time and costs.
What is bioavailability?
The rate and extent to which the active ingredient or active moiety is absorbed from a drug product and becomes available at the biological system site.
What factors affect bioavailability?
The movement of the drug in the biological system is influenced by many factors such as routes of administration, physicochemical drug properties, physiological factors (e.g. gastrointestinal pH, gastric emptying, small intestinal transit time, bile salt, absorption mechanism, food, metabolism), manufacturing technique, dosage form, and excipients. Understanding the interrelationship of these factors leads to biopharmaceutical and science-based drug product developments.
Why is the oral bioavailability of drugs less than 100%?
Incomplete oral absorption could be due to poor solubility, poor intestinal permeability, or presystemic metabolism. Incomplete oral bioavailability can often be surmounted through formulation efforts.
How do you increase oral bioavailability?
We can enhance the oral bioavailability through formulation efforts using solubilizers, pH adjustment, cosolvents, complexing agents, permeation enhancers, and enabling technologies (solid dispersion, particle size reduction and lipid-based drug delivery systems).
br>By identifying potential limiting steps for oral absorption of a compound (including dissolution, solubility, permeability, and limited metabolism process), understanding the physicochemical properties of a compound, recognizing physiological processes affecting drug absorption, along with awareness of a drug's BCS and DCS characteristics, pharmaceutical scientist can better predict formulation approaches that can maximize the drug’s bioavailability.
Why is formulation development required at the preclinical drug development stage?
Formulations play a crucial role in assessing the biological properties of a molecule during drug discovery. Maximizing exposure is the primary objective of early animal experimentation to avoid discarding developable compounds with the desired pharmacologic properties.
Diversity in the physiology between various animal species, routes of administration, limited compound amount, and limitations posed by specific pharmacological models make formulation development much more challenging. Consistency in the exposure is also a key aspect as significant variations are observed in early NCE batches.
Additionally, preclinical tox (GLP) studies at early development, require NCE formulations that are simple, robust, provide ease of preparation, convenient to deliver to animals with minimal ancillary effects of vehicle and provide provision of high and dose-related systemic exposures in animals relative to anticipated human exposures to facilitate determination of tox profiles.
The selection and development of effective formulation and drug delivery strategies are essential to achieve this.
How does Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services ensure regulatory compliance in its GLP bioanalysis CDMO offerings?
"Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services ensures regulatory compliance in its Good Laboratory Practice (GLP) bioanalysis CDMO offerings by strictly adhering to international guidelines and industry best practices. Our GLP and non-GLP bioanalysis CDMO services are conducted in fully accredited, state-of-the-art laboratories that meet the rigorous standards set by global regulatory bodies such as the US FDA, EMA, and MHRA.
We employ validated bioanalytical methods to support pharmacokinetics, toxicokinetics, and biomarker studies, ensuring that the data generated is reliable and reproducible. Our GLP bioanalysis services are performed in compliance with GLP regulations, guaranteeing the integrity and traceability of all results for regulatory submissions. Additionally, we offer non-GLP bioanalysis services for early-stage drug development, providing critical data to guide decision-making before formal GLP studies.
Aurigene's dedicated quality assurance teams oversee every aspect of the bioanalysis process, from study design to data analysis, ensuring full compliance with all applicable regulations. This robust infrastructure and adherence to GLP standards support our clients in achieving successful IND filings and progressing their drug candidates efficiently through the preclinical phase."
What distinguishes Aurigene's GLP bioanalysis services in supporting IND-enabling studies?
"Aurigene’s GLP bioanalysis services stand out in supporting IND-enabling studies through a combination of scientific expertise, state-of-the-art infrastructure, and strict adherence to regulatory standards. Our GLP and non-GLP bioanalysis services are designed to provide reliable and accurate pharmacokinetic, toxicokinetic, and biomarker data, which are essential for preparing Investigational New Drug (IND) submissions.
What sets us apart is our deep experience in tailoring bioanalysis strategies to meet the specific needs of each drug candidate. Our GLP bioanalysis services are conducted in fully accredited facilities, ensuring compliance with international regulations such as those set by the US FDA and EMEA. We use validated methodologies and high-sensitivity instruments to generate data that meets the highest standards of accuracy and reproducibility.
Moreover, we integrate non-GLP bioanalysis services for early-phase studies, providing critical data in the early stages of drug development to guide decision-making before advancing to formal GLP studies. This comprehensive approach ensures that our clients receive high-quality, regulatory-compliant data to support their IND submissions, accelerating the progression of their drug candidates through the preclinical phase."
You are about to leave Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services and affiliates website. Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services assumes no responsibility for the information presented on the external website or any further links from such sites. These links are presented to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement by Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services.
If you wish to continue to this external website, click Proceed.


Leaving already?
Don't forget to join us at
CPHI Worldwide 2023.
October 24th-26th, 2023 | Barcelona, Spain
Get ready to accelerate your drug’s journey to the market