

DMPK studies play a crucial role in drug discovery for optimizing the drug-like properties of compounds or drug molecules. They enable researchers to rank compounds based on favorable pharmacokinetic properties associated with absorption, distribution, clearance, elimination (ADME) and DDI potential. The in-vitro assays and in-vivo animal studies provide information to optimize the properties of the molecules at the early screening level and identify a drug candidate in the lead optimization phase of drug discovery. DMPK property assessment of molecules also helps in supporting or designing toxicological studies, supports safety evaluations in humans prior to first dose and helps to scale up the observed data to the human in the clinical situation.
Absorption Studies
These studies provide information on the extent and mechanism of absorption of the drug from the site of administration such as oral, nasal, dermal or any other extravascular routes of administration into the blood stream. This is crucial in determining the dose and regimen of the drug. For most orally administered drugs, absorption occurs mainly from the small intestine. The assessment of the absorptive properties of the compound includes the measurement of its permeability by means of passive diffusion or active transport (carrier mediated transport).
Assays to measure the properties influencing the absorption of the compound include solubility (kinetic and thermodynamic), measurement of permeability through artificial membrane based assays like PAMPA and cell based assays like Caco-2, MDCK.
Distribution Studies
Once the compound is absorbed, the blood stream transports it throughout the body. The distribution of drug molecules is determined by their physicochemical properties, their ability to permeate into underlying tissues and also the rate of blood flow to the tissues. Along with these, the binding pattern of compounds to proteins and their susceptibility to drug transporters also influence the distribution pattern of the drug.
DMPK studies to measure drug distribution include in-vitro plasma protein binding measurements, drug partitioning into the blood cells, in-vitro uptake/efflux transporters susceptibility, barrier tissue models, in-vivo tissue distribution etc.
Metabolism Studies
Xenobiotics are eliminated or excreted from the body by chemical alteration to make them relatively more polar to be effectively removed through excretory pathways. This process is known as metabolism and mainly takes place in the liver by groups of families of enzymes known as CYP 450. Assessing the metabolic properties of molecules helps in efficiently clearing the compound from the body. Assays include metabolic stability in liver microsomes and hepatocytes, CYP inhibition, CYP induction, drug-drug interaction studies (DDI), metabolite assessment etc.
Excretion Studies
After metabolism, the drug either changed or unchanged, gets eliminated from the body by means of excretory pathways through urine, bile, faeces, sweat etc. These processes can be passive or active depending upon the compound’s properties. Assays include urinary and faecal excretion, biliary excretion and mass balance studies employing cold or hot ligands.
Latest Posts
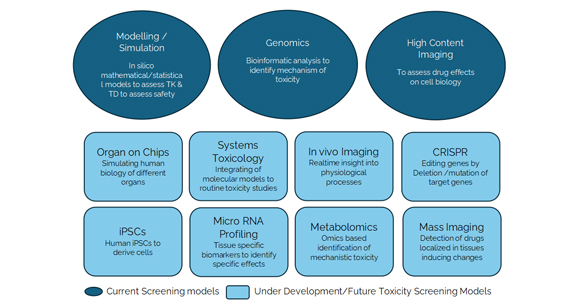
Good practices in non-clinical toxicology assessment to accelerate IND and NDA Submissions
You are about to leave Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services and affiliates website. Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services assumes no responsibility for the information presented on the external website or any further links from such sites. These links are presented to you only as a convenience, and the inclusion of any link does not imply endorsement by Aurigene Pharmaceutical Services.
If you wish to continue to this external website, click Proceed.


Leaving already?
Don't forget to join us at
CPHI Worldwide 2023.
October 24th-26th, 2023 | Barcelona, Spain
Get ready to accelerate your drug’s journey to the market





Comments Pritam
apsladmin
Permalink
apsladmin
Friday, December 9, 2022 - 14:04
This is a demo comment